Summary:
Think of dentists, and ‘teeth’ is the first thing many think of.
But what if we told you that your gum is also a vital concern for smile professionals?

Yes, it’s true! A healthy gum = a healthy smile. It holds your teeth more firmly and gives you a confident appeal. Sadly, gum or periodontal disease and periodontitis are common among 47.2% of all adults aged 30 years and above.
Interestingly, however, there’s a way to care for your gums and keep such diseases at bay. Keeping the same in mind, this blog explores:
- Periodontitis – The Gum Disease You Should Know Of!
- Different Stages of Gum Disease
- 5 Early Signs of Periodontitis
- Treatment Options for Gum Issues
Continue reading as we learn more about periodontitis in the following sections.
Periodontitis – The Gum Disease You Should Know Of!
Periodontitis, commonly known as gum disease, is a severe infection that can cause tooth loss. This gum disease attacks the tissue that keeps the teeth in place.
It is a consequence of germs or sticky, white plaque accumulating on teeth and gums, typically caused by poor dental hygiene, such as forgetting to brush or floss effectively. As a result, bones and teeth may sustain considerable damage.
Fortunately, you may stop the damage if you promptly treat periodontitis and begin practicing oral care at home. But before you know more about it, let’s understand the different stages of periodontitis.
Different Stages of Gum Disease
Stage I – Plaque Attack
Now that you’re familiar with gingivitis, it’s time to understand the first stage of the disease. It is generally caused due to plaque accumulation on the teeth and gumline.
Gingivitis is the early stage of periodontitis. If your dentist diagnoses you with gingivitis, the treatment choices are typically minimally invasive. It may be reversed with a professional dental cleaning and a consistent brushing and flossing program.
Stage II – Bone Burrowing
Periodontitis is the advanced stage of periodontitis. According to the dentists in Farmington, New Mexico, periodontitis may still be treated.
However, your oral experts may need to employ more intrusive methods, such as scaling and deep cleaning your root surfaces or removing bacteria and dirt beneath your gumline.
Interestingly, periodontitis affects more than just your gums. It may also result in bone and tissue loss throughout the mouth. If this has already happened, your dentist may refer you to a periodontist, who can propose more sophisticated operations to help repair the bone and tissue you’ve lost.
Stage III – Aggressive Periodontitis
Aggressive gum disease periodontitis is the final stage of your gum crisis. At this time, your gum pockets force the tissue to pull away from your teeth. This dissociation might cause your teeth to become loose and fall out.
5 Early Signs of Periodontitis
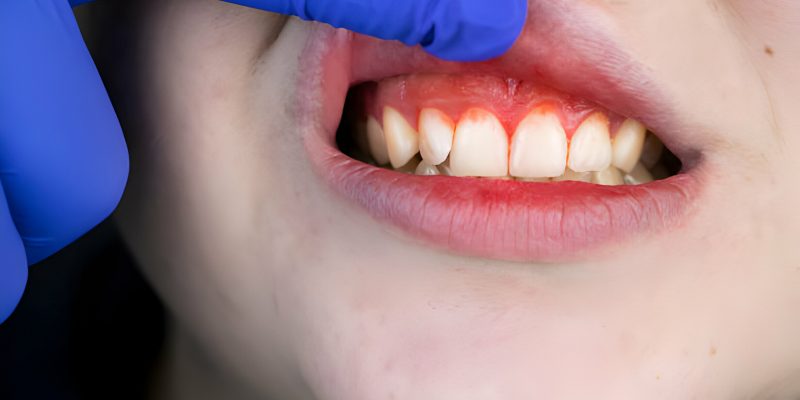
#1 Red or Swollen Gums
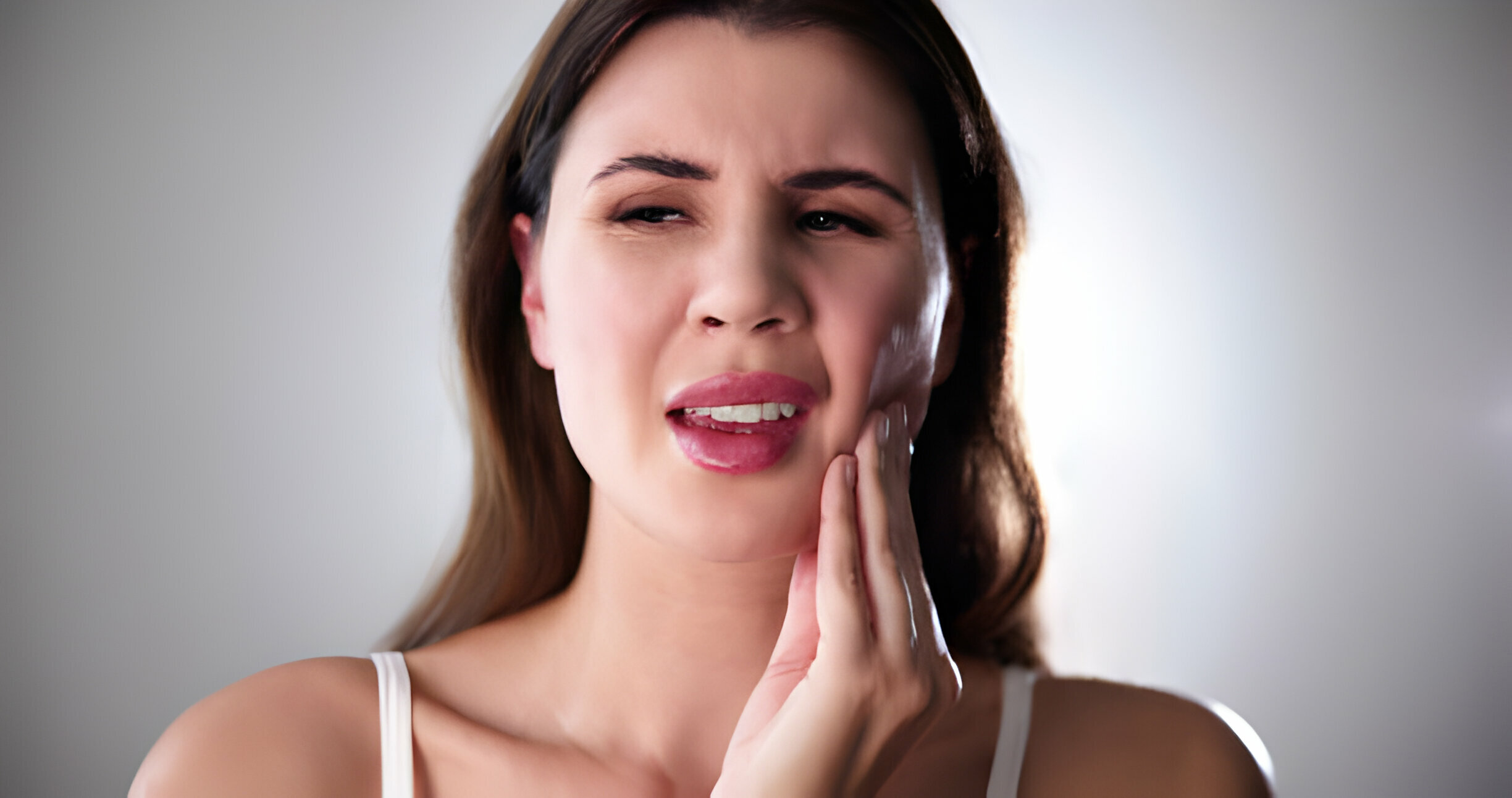
Redness and swelling are two early indicators of gum disease or gingivitis. You may detect swelling in a specific spot or across your gum line. Inflammation or swelling is produced by irritation from germs and tartar buildup on the teeth. Swollen gums are likely sensitive and painful to both hot and cold conditions.
#2 Bleeding
Flossing or brushing your teeth should not cause gum bleeding. It is another typical early indication of gum disease symptoms. It’s a significant warning sign, but we can quickly restore your dental health with the proper treatment. So, if you spot blood while brushing, notify your dentist.
#3 Bad Breath
Chronic foul breath, often known as halitosis, might indicate periodontitis. It results in gum pockets, accumulating odor-causing bacteria in your cavity. A thorough cleaning can help to repair these bacteria-filled crevices.
#4 Loose Teeth
Loose teeth are another infected gum symptom. Bacteria attack the fibers and bone that support your teeth in this phase of severe periodontitis, resulting in exposed teeth due to receded gums. This might cause your teeth to move or loosen, altering your bite. If vigorous therapy fails to salvage the loose teeth, they may have to be removed.
#5 Receding Gum Line
If you’re wondering if your gums are receding, you can tell by glancing at your teeth. Do they appear longer? This might be an indicator of receding gums. By the time this symptom emerges, your periodontitis has advanced to a terrible stage.
The tooth root may become exposed when the gums recede, making it susceptible to germs and decay. At this stage, treatment options include scaling, root planing, and antibiotics. If the gum recession is severe enough, a graft may be required to reconstruct the gum line.
Treatment Options for Gum Issues
Suppose you’re vigilant about your gum and have been able to identify periodontal disease treatment at an early stage. In that case, you can easily follow any treatment options to slow down the damage.
Good Oral Hygiene
Having good oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of periodontitis.
Here are some tips for maintaining good oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth twice a day.
- Schedule an appointment with your dentist regularly.
- Avoid using tobacco.
- Floss and use soft picks or interdental brushes.
Scaling and Cleaning
Removing calculus and plaque from your oral cavity can be an effective measure for gum disease treatment. It helps you restore periodontal health to a great extent.
Here are some tips to help you effectively clean and scale your cavity:
- Fluoride-based tooth treatment.
- Scaling and debridement to clean the teeth’s surfaces.
- Polishing to smooth rough surfaces on the teeth to avoid plaque accumulation.
Opting for scaling and cleaning treatment directly depends on the tartar and plaque accumulation in your oral cavity.

Medications
Much like visiting a professional, you can also use several medicated mouthwashes, among other treatment options.
Here’s an overview of the different medications:
- Products containing chlorhexidine (an antibacterial chemical).
- Your dentist can insert minocycline hydrochloride microspheres into pockets to prevent plaque accumulation.
- You may also use oral antibiotics in some circumstances.
Surgery
Surgery is often the last option to treat the disease of gums. Dentists generally suggest opting for surgery if you’re having severe periodontitis and require immediate assistance.
Opting for a surgery can help you:
- Remove plaque bacteria from pockets.
- Remove bacteria from the roots (where the roots of teeth split).
- Regenerative therapies can help repair damaged gum tissue and bone.
Your dentist might carry out these procedures under local anesthesia.
Takeaway
- Periodontitis, often known as gum disease, is a serious infection that can result in tooth loss.
- Periodontitis damages the tissues that hold the teeth in place.
- Redness and swelling are two early signs of periodontitis or gingivitis. You may notice swelling in a specific area or along your gum line.
- Notice a possible symptom of gum issue? Wait no more; connect with our professionals at Sundance Smiles today!